CS188 Notes I
intro
CS188作为Berkeley的人工智能基础课,你交将其精简移植后变成AU3323,课程内容大打折扣但课时并未减少多少。相比于原课程,缺失的内容——RL, Bayes’Nets, Decision Networks的课程笔记将在这里记录。
课程link:CS188
RL
概述
Still assume a Markov decision process (MDP), but we don’t know T or R.
Model-based learning
Learn an approximate model based on experiences. Solve for values as if the learned model were correct
- Learn empirical MDP model
- Solve the learned MDP
- Run the learned policy
Model-free learning
Learner is “along for the ride”.
No choice about what actions to take.
Just execute the policy and learn from experience.
Direct Evaluation
Every time you visit a state, write down what the sum of discounted rewards turned out to be and then average those samples.
It wastes information about state connections and takes a long time to converge.
Temporal Difference Learning
Sample Value
Begin by initializiing . At each step, obtain a sample value:
Exponential moving average
核心思想:Forgets about the past (distant past values were wrong anyway。
Or,
Problems
- TD学习依赖于 单步更新,而不是整个轨迹的回报,可能会导致较大的方差和更新不稳定。在某些情况下,TD方法可能 收敛慢 或 不收敛,特别是当学习率选择不当时。
- TD方法的性能高度依赖于策略,特别是在 on-policy 方法(如 SARSA)中,若探索不足(即没有充分尝试不同状态),可能会收敛到次优解。
Q-Learning
直接学习状态的q值,而不需要知道任何值、过渡函数或奖励函数。因此,Q-learning是完全无模型的。
- Receive a sample (s, a, s’, r)
- Consider your old estimate.
- Consider your new sample estimate:
- 加入学习率:
Q-learning can learn the optimal policy directly even by taking suboptimal or random actions. This is called off-policy learning (contrary to direct evaluation and TD learning, which are examples of on-policy learning).
Exploration & Exploitation
- greed
- probability, act randomly
- probability, act on current policy.
Exploration Functions
Explore areas whose badness is not(yet) established, eventually stop exploring.Takes a value estimate u and a visit count n, and Returns an optimistic utility:
Modified Q-update:
Regret
如果我们从一开始就在环境中采取最佳行动所积累的总奖励与我们通过运行学习算法所积累的总奖励之间的差异。
Approximate Q-Learning
Q 学习只是以表格形式存储状态的所有 Q 值,考虑到大多数强化学习应用都有数千甚至数百万个状态,这种方式并不是特别有效。这意味着我们无法在训练期间访问所有状态,即使我们可以存储所有 Q 值,但由于内存不足,我们也无法存储所有 Q 值。因此,我们需要 Generalize:
- Learn about some small number of training states from experience.
- Generalize that experience to new, similar situations.
Solution: - Describe a state using a vector of features (properties)
- Write a q function (or value function) for any state using a few weights :
- Difference:
- Approximate Q’s:
Policy Search
Often the feature-based policies that work well (win games, maximize utilities) aren’t the ones that approximate V / Q best.
Solution: learn policies that maximize rewards, not the Q values that predict them.
Method: start eith a ok solution then hill-climbing.
BN
Representation
CI(Conditional Independence)
and conditionally independent, iff:
Or,
BN Semantics
一种使用简单的局部分布(条件概率)描述复杂联合分布(模型)的技术。
- graphical models
- how variables locally interact
- Local interactions chain together to give global, indirect interactions
Formulation:
- 有向无环图.
- A conditional distribution for each node P(X|A1…An)P(X|A1…An), where AiAi is the ith parent of XX, stored as a conditional probability table or CPT. Each CPT has n+2n+2 columns: one for the values of each of the nn parent variables A1…AnA1…An, one for the values of XX, and one for the conditional probability of XX given its parents.
联合分布:
D-separation
一个变量是否独立于另一个变量,或者在给定第三个随机变量的情况下,一个随机变量是否条件独立于另一个随机变量。贝叶斯网络联合概率分布的表示为我们提供了一种通过检查图的拓扑结构来快速回答此类问题的方法。
D-separation 是一种仅通过研究图来回答条件独立查询的条件/算法
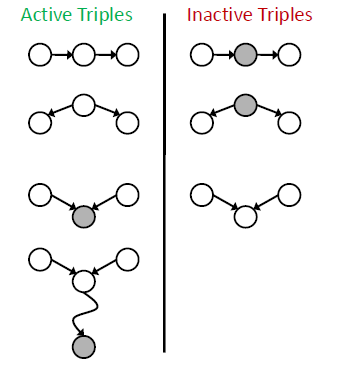
三元组
分析三元组,如果是 active 的,那么 X 与 Y 就不独立
如果是 Inactive 的,那么 X 与 Y 就是(条件)独立的。
在实际图中,找到 X 与 Y 之间的所有路径,画出三元组,满足:
- 所有路径都是 inactive 的。
- 路径 inactive 指的是路径上存在 inactive 的三元组。
那么 X 与 Y 是条件独立的。
给定所有父节点,则此节点与他的所有父节点条件独立。