Intro
Search: Formulation and Solution (s)
Agent categories
Rational agent
Reflex agent
Planning agent
Have the model of how the world evolves.
Optimal and replannning.
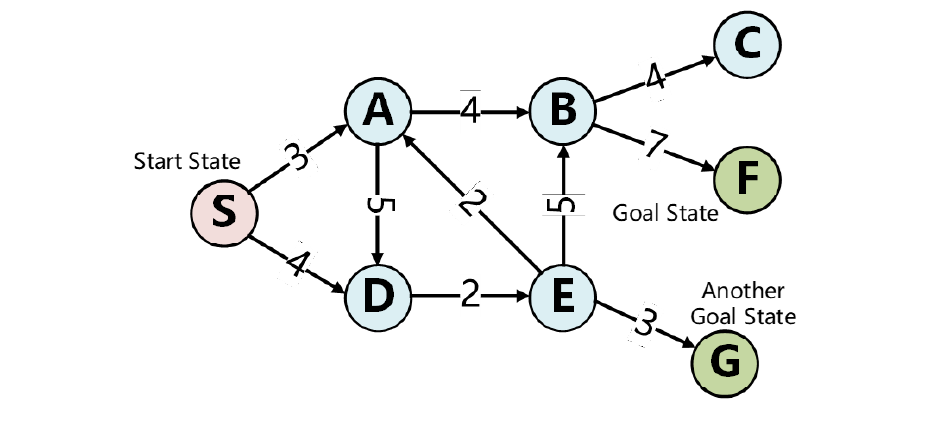
Basic Elements of Search Problem
State Space
Successor Function
Start state (to start the search) and goal test (to terminate the search)
Solution
Search graph
A mathematical formulation of Search Problem: G={V, E}
Nodes V: States IN State Space
Edges/Arcs E: Successor Functions from states to successors;
We still have a start state and goal test
Solution: Path on the state graph from the start state to pass the goal test.
Issues:
In a state space graph, each state occurs only once!
We can rarely build this full graph in memory
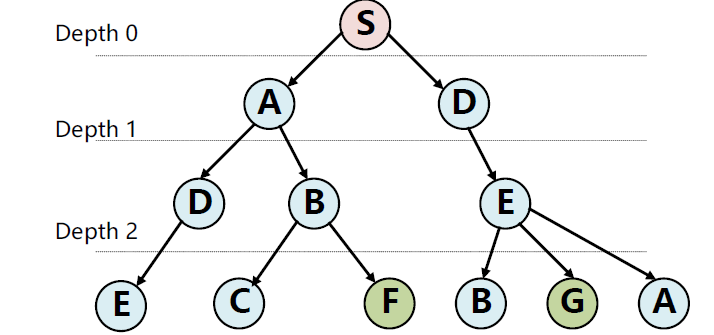
Search tree
To unravel a graph into a tree, choose a root node and trace every path from that node until you reach a leaf node or a node already in that path.
Partial Plan: From S to current state
Expansion: Add a new state to partial plan
Fringe: A queue of partial plans under consideration
Exploration Strategy: Choose partial plan in fringe for Expansion.
Solutions
Evaluations
Strategies are evaluated along the following dimensions
Completeness: Find a solution or not?
Time Complexity: Number of expansion.
Space Complexity: Max number of nodes in memory.
Measured by:
b: max branching factor of the search tree;
d: depth of the least-cost solution;
m: max depth of the state space;
Optimality: Find the least-cost solution or not?
DFS
DFS 算法需要注意移除 Path 中相同的 State,防止陷入无限循环。
Completeness: Yes;
Optimality: No ;
Time Complexity: O (b m b^m b m
Space Complexity: O (bm);
code diaplay:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 def depthFirstSearch (problem ): "*** YOUR CODE HERE ***" path = util.Path([problem.getStartState()], [], 0 ) if problem.isGoalState(problem.getStartState()): return [] fringe = util.Stack() fringe.push(path) while not fringe.isEmpty(): current_path = fringe.pop() current_loc = current_path.locations[-1 ] if problem.isGoalState(current_loc): return current_path.actions else : successors = problem.getSuccessors(current_loc) if bool (successors): for successor in successors: next_loc = successor[0 ] next_action = successor[1 ] next_cost = successor[2 ] if next_loc not in current_path.locations: locations = current_path.locations[:] locations.append(next_loc) all_actions = current_path.actions[:] all_actions.append(next_action) next_cost = current_path.cost + next_cost path = util.Path(locations, all_actions, next_cost) fringe.push(path) return []
BFS
Fringe 中 Partial Solution 的 Path 长度较短的出队优先级较高
Completeness: Yes;
Optimality: Yes (仅当状态间转移 Cost=1 时成立);
Time Complexity: O (b d b^d b d
Space Complexity: O (b d b^d b d
code display:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 def breadthFirstSearch (problem ): """Search the shallowest nodes in the search tree first.""" "*** YOUR CODE HERE ***" path = util.Path([problem.getStartState()], [], 0 ) if problem.isGoalState(problem.getStartState()): return [] fringe = util.Queue() fringe.push(path) while not fringe.isEmpty(): current_path = fringe.pop() current_loc = current_path.locations[-1 ] if problem.isGoalState(current_loc): return current_path.actions else : successors = problem.getSuccessors(current_loc) if bool (successors): for successor in successors: next_loc = successor[0 ] next_action = successor[1 ] next_cost = successor[2 ] if next_loc not in current_path.locations: locations = current_path.locations[:] locations.append(next_loc) all_actions = current_path.actions[:] all_actions.append(next_action) next_cost = current_path.cost + next_cost path = util.Path(locations, all_actions, next_cost) fringe.push(path) return []
Always expand the least-cost unexpanded first
Completeness: Yes
Optimality: Yes
Time Complexity: O (b 1 + ⌊ C ∗ + ϵ ⌋ b^{1+\lfloor C^*+\epsilon \rfloor} b 1 + ⌊ C ∗ + ϵ ⌋
Space Complexity: O (b 1 + ⌊ C ∗ + ϵ ⌋ b^{1+\lfloor C^*+\epsilon \rfloor} b 1 + ⌊ C ∗ + ϵ ⌋
code diaplay:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 def uniformCostSearch (problem ): """Search the node of least total cost first.""" "*** YOUR CODE HERE ***" path = util.Path([problem.getStartState()], [], 0 ) if problem.isGoalState(problem.getStartState()): return [] fringe = util.PriorityQueue() fringe.push(path,path.cost) while not fringe.isEmpty(): current_path = fringe.pop() current_loc = current_path.locations[-1 ] if problem.isGoalState(current_loc): return current_path.actions else : successors = problem.getSuccessors(current_loc) if bool (successors): for successor in successors: next_loc = successor[0 ] next_action = successor[1 ] next_cost = successor[2 ] if next_loc not in current_path.locations: locations = current_path.locations[:] locations.append(next_loc) all_actions = current_path.actions[:] all_actions.append(next_action) next_cost = current_path.cost + next_cost path = util.Path(locations, all_actions, next_cost) fringe.push(path,path.cost) return []
Depth-Limited Search (DLS)
Early stop with limited depth
时间复杂度为 O ( b l (b^l ( b l
空间复杂度为 O (b l bl b l
Iterative Deepening Search (IDS)
如果其状态空间大小为 m,则从 1 开始,逐步增加 DLS的最大搜索深度,直到 m,如果在这过程中找到解,则停止搜索。其基本过程是 BFS 和 DFS 的结合,相比于 DFS,避免了过度陷入较深的层;相比于 BFS,避免了从第一层到当前层每一个节点的拓展。
Completeness: Yes, we need to avoid duplication along the path.
Optimality: Yes, if step cost = 1.
Time Complexity: O(b d b^d b d
Space Complexity: O(bd)
Completeness
Optimality
Time Complexity
Space Complexity
DFS
Yes
No
O (b m b^m b m
O (bm)
BFS
Yes
Only when cost =1
O (b d b^d b d
O (b d b^d b d
UCS
Yes
Yes
O (b 1 + ⌊ C ∗ + ϵ ⌋ b^{1+\lfloor C^*+\epsilon \rfloor} b 1 + ⌊ C ∗ + ϵ ⌋
O (b 1 + ⌊ C ∗ + ϵ ⌋ b^{1+\lfloor C^*+\epsilon \rfloor} b 1 + ⌊ C ∗ + ϵ ⌋
DLS
No
No
O ( b l (b^l ( b l
O ( b l (bl ( b l
IDS
Yes
Only when cost =1
O (b d b^d b d
O (bd)
ILS
Yes
Yes
O (b 1 + ⌊ C ∗ + ϵ ⌋ b^{1+\lfloor C^*+\epsilon \rfloor} b 1 + ⌊ C ∗ + ϵ ⌋
O (b ( 1 + ⌊ C ∗ + ϵ ⌋ ) b(1+\lfloor C^*+\epsilon \rfloor) b ( 1 + ⌊ C ∗ + ϵ ⌋)
启发式搜索的目的是通过引入Heuristics 针对 Forward Cost 进行估计,提高搜索效率
Heuristics
启发式函数,(Heuristics),是针对当前状态 n 到 Goal State 之间最短路径的估计,一般用 h (n) 表示。H (n) 一般满足以下性质:
h (n) ≥ 0 for all states;
h (n) = 0,则 n 到达了终点;
h (n) = ∞,则 n 则无法到达终点;
Greedy Searchl (贪心法)
对于当前的需要考虑的 Successors,通过 f (n) = h (n) 排序,选取最小的 f (n) 对应的状态(与终点最近的状态)进行 Expand。
A* search
本质上是UCS 和GBFS 的结合,采用Priority Queue 维护Partial Solution;Priority Queue 中的元素优先级由f(n) = g(n)+h(n) 决定,其中g(n)的定义与UCS 中一致;h(n) 则是启发式函数;出队入队过程与上文中的Uninformed Search 完全一致。
Admissible:if0 ⩽ h ( n ) ⩽ h ∗ ( n ) 0\leqslant h(n)\leqslant h^*(n) 0 ⩽ h ( n ) ⩽ h ∗ ( n )
这里可以看到,h(n) 对于我们的算法而言,希望能够更好地接近h∗(n) 真值。当我们越接近时,就能够更高效地找到最优解。
只有当h(n)是admissible的,A*算法才是最优的。
code display:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 def aStarSearch (problem, heuristic=manhattanHeuristic ): """Search the node that has the lowest combined cost and heuristic first.""" "*** YOUR CODE HERE ***" path = util.Path([problem.getStartState()], [], 0 ) priority=path.cost+heuristic(path.locations[-1 ],problem) if problem.isGoalState(problem.getStartState()): return [] fringe = util.PriorityQueue() fringe.push(path,priority) while not fringe.isEmpty(): current_path = fringe.pop() current_loc = current_path.locations[-1 ] if problem.isGoalState(current_loc): return current_path.actions else : successors = problem.getSuccessors(current_loc) if bool (successors): for successor in successors: next_loc = successor[0 ] next_action = successor[1 ] next_cost = successor[2 ] if next_loc not in current_path.locations: locations = current_path.locations[:] locations.append(next_loc) all_actions = current_path.actions[:] all_actions.append(next_action) next_cost = current_path.cost + next_cost path = util.Path(locations, all_actions, next_cost) priority=path.cost+heuristic(path.locations[-1 ],problem) fringe.push(path,priority) return []